Neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS), and Prion disease are known to be caused by the formation and accumulation of misstructured (misfolding) proteins, and these are collectively called “conformational diseases”.
Our company is promoting research and development of both diagnosis and treatment on conformational diseases.
Our company is promoting research and development of both diagnosis and treatment on conformational diseases.
Development of probe for diagnostic imaging
As a diagnostic method for conformational disease, PET (Positron Emission Tomography) is considered to be effective for detecting the causative aggregate protein. For example, in Alzheimer's disease (AD), several PET probes have been developed for detecting amyloid β and tau which are known as causative aggregate proteins. However, there are many other diseases in which the aggregate proteins have been identified but still no probes to detect them have been developed.
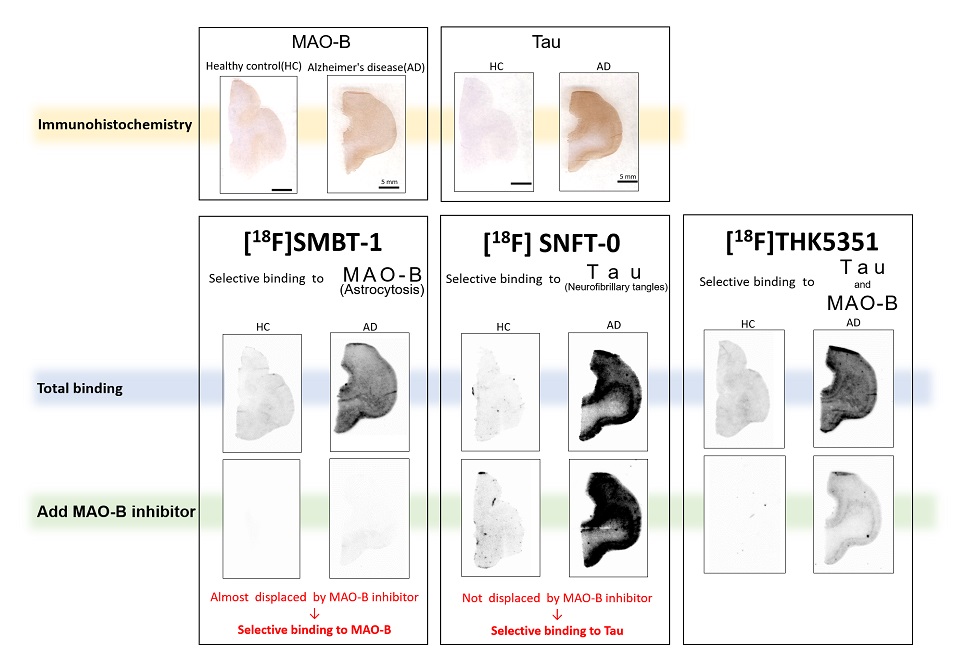
On the other hand, in neurodegenerative diseases, astrocytes being one of glial cells increase in the central nervous system. The enzyme "Monoamine oxidase-B (MAO-B)" present in the mitochondrial membrane of the astrocytes is regarded as an index of neuroinflammation or neurodegenerative disease such as AD and considered to be a diagnostic index of diseases for which other probes have not been developed. And in addition to neurodegenerative diseases, astrocytes are known to also increase in various neurological diseases such as cerebrovascular disorders, traumatic brain injury, and epilepsy. By using MAO-B as a diagnostic index, we expect that early diagnosis of these neurological diseases and understanding of their symptoms will become possible.
On the other hand, in neurodegenerative diseases, astrocytes being one of glial cells increase in the central nervous system. The enzyme "Monoamine oxidase-B (MAO-B)" present in the mitochondrial membrane of the astrocytes is regarded as an index of neuroinflammation or neurodegenerative disease such as AD and considered to be a diagnostic index of diseases for which other probes have not been developed. And in addition to neurodegenerative diseases, astrocytes are known to also increase in various neurological diseases such as cerebrovascular disorders, traumatic brain injury, and epilepsy. By using MAO-B as a diagnostic index, we expect that early diagnosis of these neurological diseases and understanding of their symptoms will become possible.
We have so far developed a PET probe "[18F]THK5351" that detects both MAO-B and tau for diagnosis of AD. With this probe as the point of start, currently, we are developing PET probes that specifically and selectively detect MAO-B and tau separately.
As one of such selective PET probes to detect MAO-B, we have developed "[18F]SMBT-1". Currently, its exploratory clinical research is underway, and promising data has been obtained. For another PET probe selective to tau, we have developed "[18F]SNFT" and are now preparing for its exploratory clinical research in the near future.
Development of vaccine treatment
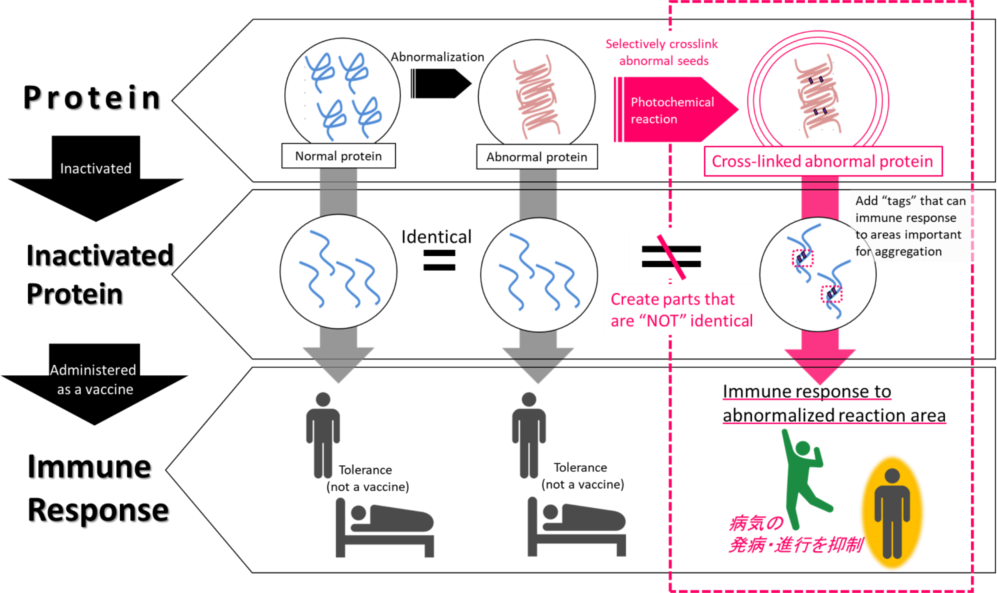
In order to establish a treatment method for conformational diseases, research and development of methods for inhibiting and eliminating protein aggregates has been actively carried out, but it is extremely difficult because the chemical structure of misfolding proteins is not clear.
Therefore, in this study, we focused on a protein seed that is the core of misfolding protein aggregates. So far, the chemical structure of this seed has not been clarified except that it is an oligomer rich in β-sheet structure, and no specific treatment has been established yet. In addition, the seed was not recognized as non-self even when inactivated, and because the immune response was tolerated, it could not be used as a vaccine. In this method, we aim for producing specific antibodies to inhibit and eliminate the seed by using a “tagged” seed that is cross-linked by applying a unique photochemical reaction technology and has an immune response to inactivated protein and then use it as a vaccine.
At present, we are conducting research with the aim of establishing active immunotherapy that produces specific antibodies that inhibit or eliminate the seed generation by administration of vaccines and passive immunotherapy that enables treatments by administering the specific antibodies created through this technology.